AI Sports Betting: The Definitive Guide to Predictive Modeling

Key Takeaways
- The Signal vs. Noise Ratio: AI excels at filtering thousands of data points to find non-linear correlations that human handicappers miss, but it is susceptible to overfitting if not validated correctly.
- Predictive vs. Generative: Success in betting comes from predictive models (Random Forests, Gradient Boosting) that output probabilities, not generative LLMs that analyze text.
- Market Efficiency: The goal of AI isn't just to predict game outcomes, but to identify instances where the sportsbook's implied probability differs from the model's true probability (Positive Expected Value).
- The Data Pipeline: A robust AI betting strategy relies on four pillars
- The Limitation of History: Sports are 'non-stationary' environments; rule changes and evolving playstyles can render historical training data obsolete, requiring constant model retraining.
Definition
AI sports betting is the application of machine learning algorithms and predictive modeling to analyze historical data, identify market inefficiencies, and forecast game outcomes with higher probability than implied sportsbook odds.
Table of Contents
The era of gut feeling and "eye tests" isn't dead, but it is being aggressively outpaced. In the high-frequency trading environment of modern sportsbooks, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has shifted from a buzzword to the fundamental architecture of sharp betting. For the sophisticated bettor, AI is not a magic crystal ball—it is an industrial-grade excavator for digging up edge.
This guide moves beyond the surface-level hype. we are going to dismantle how AI actually functions in the betting ecosystem, the specific machine learning models dominating the space, and how to differentiate between signal and noise in an increasingly automated market.
The Evolution: From Linear Regression to Deep Learning#
To understand where we are, we have to look at the trajectory of sports modeling.
The Statistical Dark Ages
Historically, "models" were simple linear regressions or Elo rating systems. A bettor might have a spreadsheet weighting Points Per Game (PPG) and Home Field Advantage. These linear models assume a straight-line relationship between variables. They are robust, interpretable, but ultimately limited in capturing the chaotic non-linearity of sports.
The Machine Learning Revolution
The modern edge comes from Machine Learning (ML). Unlike static formulas, ML algorithms learn from data. They iterate. If a model predicts the Chiefs to cover and they fail, the algorithm adjusts its internal weights to reduce that error in the next iteration.
We are currently seeing a massive shift toward "Black Box" models—specifically Neural Networks and Gradient Boosted Trees. These models can ingest thousands of features—from player biomechanics to wind patterns—and detect complex, non-linear interactions that a human handicapper would never see.
How AI Sports Betting Models Work#
Building a predictive AI for sports betting is a pipeline problem. It requires four distinct stages: Data Ingestion, Feature Engineering, Modeling, and Execution.
1. Data Ingestion (The Raw Fuel)
Garbage in, garbage out. The best models don't just use box scores. They ingest:
- Play-by-play data: Granular events (e.g., success rate of a rush to the left tackle).
- Computer Vision data: Player tracking data (like NFL Next Gen Stats or NBA Second Spectrum) that tracks x/y coordinates of every player 25 times per second.
- Market data: Real-time odds movement from sharp books (like Pinnacle or Circa) to understand market sentiment.
2. Feature Engineering (The Secret Sauce)
This is where the math meets the sport. Raw data is useless until it is transformed into a "feature."
- Raw Data: LeBron James scored 30 points.
- Feature: LeBron James’ scoring variance against top-5 defensive ratings when playing on 2 days of rest.
The goal is to create features that have high predictive power regarding the target variable (the game outcome or spread).
3. Model Training & Validation
The dataset is split into "Training" (historical data) and "Testing" (unseen data). The AI trains on the history and tries to predict the test set.
Common algorithms used by syndicates include:
- Random Forests: Builds a "forest" of decision trees to average out errors and reduce overfitting.
- XGBoost / LightGBM: Gradient boosting frameworks that are exceptionally fast and effective at structured data (like sports stats).
- LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) Networks: A type of Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) specifically designed for sequence prediction, making them ideal for analyzing a team's form over a season.
4. Backtesting vs. Paper Trading
A model is only as good as its backtest, but backtests are notorious liars. A common pitfall in AI betting is look-ahead bias—using data in the model that wouldn't have been available at the time of the bet (e.g., using full-game stats to predict the halftime line).
Generative AI vs. Predictive AI#
It is crucial to distinguish between the two dominant forms of AI currently making headlines.
Generative AI (LLMs like ChatGPT): These are language models. They are excellent at scraping news, summarizing injury reports, or writing code to build a scraper. However, they are generally poor at calculating probability. If you ask a standard LLM to predict a winner, it is often hallucinating based on training data text, not running a Monte Carlo simulation.
Predictive AI: These are the mathematical engines described above. They do not "speak"; they output a probability (e.g., "Home Team Win Probability: 56.4%").
The "Black Box" Problem and Interpretability#
One of the paradoxes of AI in betting is the trade-off between accuracy and interpretability.
A simple logistic regression is easy to understand: "The model likes the Eagles because their rushing yards per attempt is 2.0 standard deviations above the mean."
A Deep Neural Network is opaque. It might like the Eagles because of a complex interaction between the opposing quarterback's pressure rate and the turf type of the stadium. The user—and often the developer—cannot see why the decision was made, only that the math dictates it.
For the bettor, this requires a shift in mindset. You are no longer betting on the team; you are betting on the long-term validity of the model's error rate.
Finding the Edge: CLV and Market Efficiency#
Even the most sophisticated AI cannot simply "predict the winner." To make money, it must predict the winner better than the market.
The sports betting market is an efficient mechanism. The "Closing Line" is widely considered the most accurate representation of true probability because it reflects all available information and the weight of maximum money.
The AI Advantage
AI finds value in the latency and granularity of the market.
- Latency: Markets react to news (injuries, lineup changes). AI can process this faster than a human oddsmaker can adjust the line.
- Granularity: While the market is efficient on the NFL spread, it is less efficient on obscure prop bets. An AI model can calculate the probability of a specific running back getting over 3.5 receptions more accurately than a sportsbook manager who is focused on balancing the main lines.
This is where tools like our Live +EV Feed become critical. They utilize real-time market data to identify instances where a sportsbook's odds have drifted away from the "true price" established by sharp books and predictive models.
Limitations: Where AI Fails#
If AI were perfect, sportsbooks would cease to exist. There are massive limitations that every data-driven bettor must respect.
1. The "Non-Stationary" Problem
Sports constantly change. Rule changes (e.g., the MLB pitch clock), coaching shifts, and evolving playstyles mean that data from 2015 might be irrelevant to 2024. A model trained on 10 years of data might fail because the "game" it learned no longer exists.
2. Overfitting
This occurs when a model learns the "noise" rather than the signal. An overfitted model might find a correlation that "Teams wearing blue jerseys win 80% of games on Tuesdays." This is a statistical anomaly, not a predictive fact. When applied to future games, the model will crash.
3. The Human Element
AI struggles with "soft" factors. Locker room chemistry, a player playing through an undisclosed personal issue, or motivation in a "dead rubber" game are hard to quantify.
Building Your Tech Stack#
You do not need a PhD in Data Science to leverage AI. The modern bettor's stack involves a mix of off-the-shelf tools and custom logic.
- Scrapers: Python scripts (BeautifulSoup/Selenium) to aggregate odds.
- Database: Storing historical lines and results (PostgreSQL is standard).
- Analysis: R or Python (Pandas/Scikit-Learn) for testing hypotheses.
- Execution: Automated alerting or API integration for betting.
However, building this infrastructure from scratch is costly in both time and server fees. Most semi-pros rely on aggregated platforms to handle the heavy lifting of data ingestion, allowing them to focus on the final decision-making process.
The Future: Micro-Betting and Real-Time Inference#
The frontier of AI sports betting is In-Game Micro-Betting.
Standard live betting relies on simple algorithms. The next generation of AI will process video feeds in real-time to price outcomes like "Next Pitch: Strike or Ball" or "Next Possession: 3-Pointer."
This requires Computer Vision models running at the edge (processing data instantly rather than sending it to a cloud server). As 5G latency decreases and processing power increases, the ability to model the game state milliseconds before the sportsbook updates the odds will be the ultimate battleground for arbitrage and +EV betting.
Summary#
AI in sports betting is not about guaranteeing a win on Sunday night. It is about rigorously defining probability. It allows us to strip away biases, ignore the media narratives, and view sports as a data distribution.
Whether you are building your own Random Forest classifier or using tools like an Arbitrage Finder to exploit market discrepancies, the goal remains the same: identify a price that implies a probability lower than reality, and execute.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can AI predict sports betting results accurately?▼
What is the best machine learning model for sports betting?▼
How does AI identify value bets?▼
Is using AI for betting legal?▼
What is the difference between Generative AI and Predictive AI in betting?▼
Related Articles
Football Squares Rules: The Definitive Analytics & Strategy Guide
Master football squares with this data-driven guide. Learn the rules, optimal number probabilities, auction valuation strategies, and how to gain an edge in high-stakes pools.
.png&w=3840&q=75)
Middling in Sports Betting: The Math Behind the Most Profitable Play
Master the art of middling. Learn how to exploit line movements to create risk-free windows where you win both sides of a bet. Advanced strategy for sharps.
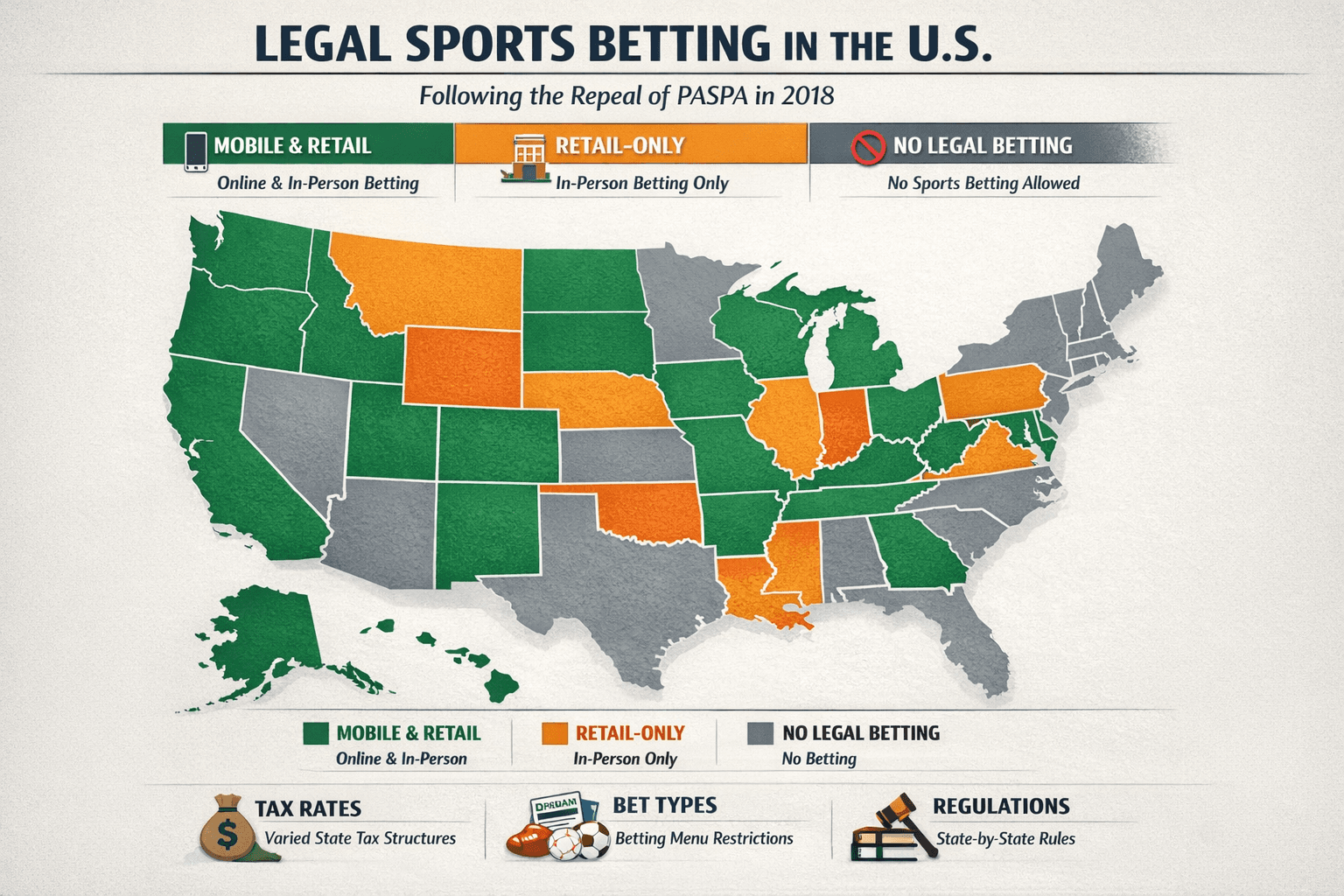
Legal Sports Betting States: 2026 Definitive Sharps Guide
The complete 2026 map of legal US sports betting. Analysis of mobile vs. retail markets, tax impact on odds, prop restrictions, and legislative forecasts.

Alt Markets Explained: Exploiting Derivatives for +EV Betting
Master alternate betting markets. Learn how sharps exploit pricing inefficiencies in alt spreads, totals, and props to find edge beyond the main lines.
Ready to find your Edge?
Join thousands of smart bettors who have stopped guessing and started calculating. Access institutional-grade tools for the price of a standard wager.
